Table of Contents
In this digital era, many entrepreneurs and businesses are looking for ways to create their products or services with limited resources and time.
This is where Minimum Viable Product (MVP) development comes into the picture.
In this blog, we will discuss what MVP is, why it is essential, the benefits of MVP development, the process to build an MVP, the cost to build an MVP, how long it takes to build an MVP, and many more.
So, with being said, let’s get right into it, starting with:
What is MVP?

MVP is a development technique where a product is developed with minimum features to satisfy early customers and validate the idea, with the least amount of effort and resources.
Moreover, it provides an opportunity to test the product in the market and receive feedback from early adopters. MVP is the first version of a product that allows businesses to test their ideas, collect feedback, and make improvements.
Why is MVP Development Important?
MVP (Minimum Viable Product) development is an essential step in the product development process. It plays a vital role in the success of entrepreneurs and businesses by allowing them to validate their ideas before investing significant amounts of time, effort, and resources into building a full-fledged product.
By creating an MVP, businesses can test their products in the market, receive feedback from users, and make necessary changes before launching the final product. This iterative process not only saves time and money, but it also helps businesses to create a better product that meets the needs of their target market.
In addition, MVP development can also help businesses to identify potential pain points and areas for improvement in the product development process. By leveraging the insights gained from MVP development, businesses can refine their product development process and create a more efficient and effective process that leads to better products and increased profitability.
How MVP helps Mobile App Development?

Mobile app development is a complex process which requires a lot of time, resources and money.
Moreover, one way to mitigate the risks involved is to follow the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) approach. MVP is a development technique that helps app developers quickly validate their ideas and test the waters before investing too much time and money in building a fully functional app.
The MVP approach involves creating a basic version of the app with only the most essential features. This allows developers to test the app’s functionality, user experience, and marketability.
Feedback from users and market research can then be used to make informed decisions about what features to add or remove.
By using the MVP approach, developers can save time and money on app development. They can also reduce the risk of building an app that does not meet the needs of users or the market.
In addition, MVP can help mobile app developers to:
- Identify potential obstacles early on
- Focus on the core features of the app
- Test the market demand for the app
- Gather user feedback and improve the app accordingly
- Reduce the time to market
MVP is a valuable approach for mobile app development that can help developers validate their ideas quickly while reducing the financial and time investment required. With the MVP approach, developers can create an app that meets the needs of their target audience and stands out in the market.
Benefits of MVP Development
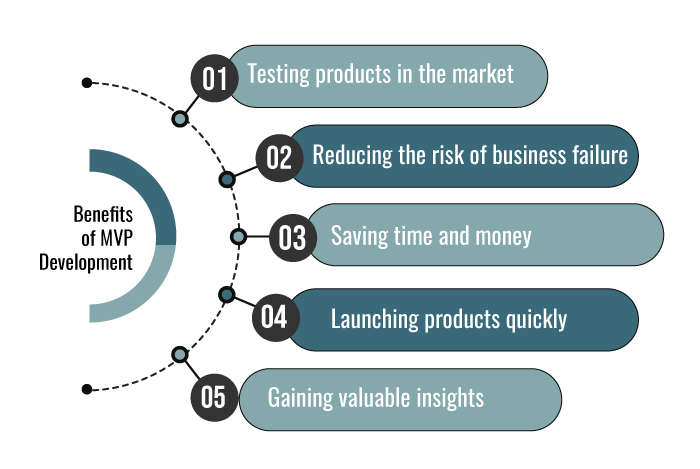
MVP development is a crucial step for businesses that want to succeed in the market. Here are some reasons why:
-
Testing products in the market
MVP development helps businesses to test their products in the market and collect feedback from early adopters. This feedback can be used to improve the product and develop new features that meet the needs of the target audience.
-
Reducing the risk of business failure
By validating ideas before investing a lot of money and resources, MVP development reduces the risk of business failure. This allows businesses to save time and money, which can then be used to focus on other important aspects of the business.
-
Saving time and money
By building only essential features, businesses can save time and money, which can then be used to focus on other important aspects of the business.
-
Launching products quickly
MVP development enables businesses to launch products quickly and stay ahead of the competition, which is crucial in today’s fast-paced business environment.
-
Gaining valuable insights
By developing an MVP, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences which can be used to improve the product and develop new features that meet the needs of their target audience.
Overall, MVP development is an essential tool for businesses that want to succeed and grow in the long run.
Process to Build an Minimum Viable Product
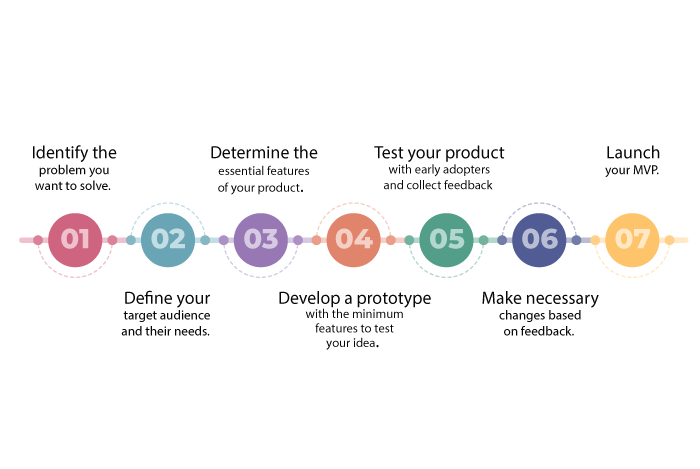
Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a crucial step in any product development process. The MVP helps you to test your product idea with a minimal investment of time and resources. Here are the essential steps to build an MVP:
1. Identify the problem you want to solve.
- Determine the problem that your product will solve and the benefits it will provide to your target audience.
- Conduct market research to identify existing solutions and potential competitors.
- Refine your problem statement to ensure that it is clear, specific, and actionable.
2. Define your target audience and their needs.
- Identify your target audience and their characteristics, such as demographics, interests, and behaviors.
- Conduct user research to understand their needs, pain points, and preferences.
- Develop user personas to help you create a product that meets the needs of your target audience.
3. Determine the essential features of your product.
- Identify the features that are necessary to solve the core problem and provide value to early adopters.
- Prioritize these features based on their importance and feasibility.
- Create a feature roadmap to guide the development process and ensure that you are building the right features at the right time.
4. Develop a prototype with the minimum features to test your idea.
- Create a low-fidelity prototype to test your product concept and validate your assumptions.
- Iterate on your prototype based on user feedback and refine the design and functionality as necessary.
- Create a high-fidelity prototype to further test and validate your product before building the MVP.
5. Test your product with early adopters and collect feedback.
- Launch your MVP to a small group of early adopters and collect feedback on their experience using your product.
- Use various methods to gather feedback, such as surveys, interviews, and user testing.
- Analyze the feedback and identify areas for improvement and further development.
6. Make necessary changes based on feedback.
- Use the feedback to make improvements to your product, such as adding new features or improving existing ones.
- Prioritize the changes based on their impact on user experience and business goals.
- Iterate on your product until you have a version that meets the needs of your target audience and provides value to your business.
7. Launch your MVP.
- Launch your MVP to a wider audience and promote it using various marketing channels.
- Monitor user feedback and engagement metrics to identify areas for improvement and further development.
- Continue to iterate on your product and add new features based on user feedback and market trends.
By following these steps, you can build an MVP that solves a real problem for your target audience, provides value to your business, and sets you up for success in the market.
What to do After You Build an MVP

After building an MVP, it is important to take the time to analyze feedback and make necessary changes. This feedback can come from a variety of sources, such as user testing, customer interviews, or analytics data. Once you have a clear understanding of what changes need to be made, you can begin to:
Improve the user experience and user interface.
- This could involve making changes to the design or layout of your product to make it more intuitive and user-friendly.
- It could also involve streamlining certain processes or workflows to make them more efficient.
Add new features based on user feedback and demand.
- This could involve adding new functionality to your product that addresses specific pain points or needs identified by users.
- It could also involve integrating with other tools or platforms to provide a more comprehensive solution.
Stay up to date with the latest industry developments.
- This could involve monitoring trends in the market to ensure that your product remains competitive.
- It could also involve keeping an eye on new technologies or innovations that could enhance your product’s capabilities.
By taking these steps, you can ensure that your product continues to evolve and improve over time, meeting the changing needs of your users and staying ahead of the competition.
Case Studies: Examples of Successful MVPs
Here are some examples of successful MVPs:
- Dropbox: Started as a simple file-sharing service with a minimum viable product that allowed users to drag and drop files into a folder, and it has since evolved into a major cloud storage provider.
- Airbnb: Began as a simple website allowing people to rent out air mattresses in their homes, and it has since expanded into a global platform for booking accommodations.
- Instagram: Initially launched as a photo-sharing app with a few basic filters, and it has since grown into one of the most popular social media platforms in the world.
By starting with a minimum viable product, these companies were able to test their ideas and validate their assumptions before investing significant resources into full product development. This approach allowed them to quickly adapt to user feedback and iterate on their product to create something that truly resonated with their target audience.
MVP vs. Full Product Development: Which is Right for You?
When deciding between MVP and full product development, it’s important to consider your goals, resources, and timeline. If you have limited resources and want to test a new idea quickly and efficiently, starting with an MVP may be the right choice. However, if you have a clear vision for your product and are able to invest the necessary resources to bring it to market, full product development may be a better option.
The key is to carefully evaluate your options and make an informed decision based on your unique situation. Remember that an MVP is not a shortcut to success and must still be thoughtfully designed and executed to be effective.
The Future of MVP Development: Trends and Predictions
Some trends and predictions for the future of MVP development include:
- Increased use of no-code and low-code tools to streamline MVP development
- Greater emphasis on user experience and design in MVP development
- More focus on sustainability and ethical considerations in MVP development
By staying informed and adapting to these trends, businesses can continue to use MVPs as a powerful tool for innovation and growth.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Building an MVP
When building an MVP, there are several common mistakes that can hinder its effectiveness and success. It is important to recognize these mistakes and take steps to avoid them.
Some common mistakes to avoid when building an MVP include:
- Trying to include too many features in the MVP
- Failing to clearly define the problem the MVP is solving
- Neglecting to gather and incorporate user feedback
- Underestimating the importance of design and user experience
Including too many features can cause the MVP to become bloated and unfocused, while failing to clearly define the problem can make it difficult to prioritize features. Incorporating user feedback is crucial for ensuring that the product meets the needs of its intended users, and neglecting design and user experience can turn users off and prevent them from fully engaging with the product.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can help ensure that your MVP is effective and successful in achieving your goals.
Cost to Build an Minimum Viable Product
Building an MVP (minimum viable product) is a crucial step in starting a new business, and it’s important to understand the costs involved. In general, the cost of building an MVP can vary greatly depending on a number of factors. For example, the complexity of the product, the features included, and the team’s experience can all have an impact on the final cost.
To start, the complexity of the product can greatly affect the cost. A simple MVP with just a few basic features will cost much less than a more complex product with many intricate features. The more complex the product, the more time and resources it will take to build, resulting in a higher cost.
Another factor to consider is the features included in the MVP. Some features are more costly to develop than others, and it’s important to prioritize which features are necessary for the MVP and which can be added later. This can help to keep costs down while still providing a functional MVP.
Finally, the team’s experience can also play a role in the cost of building an MVP. A more experienced team will likely be able to work more efficiently and effectively, resulting in a lower cost. On the other hand, a less experienced team may take longer to complete the MVP and may require more resources, resulting in a higher cost.
Taking all of these factors into account, the cost to build an MVP can range from $10,000 to $50,000 or more. It’s important to carefully consider all of the factors involved and to work with a team that has the necessary experience to build a successful MVP within your budget.
How Long Does it Take to Build an Minimum Viable Product?
When it comes to building an MVP, there are a number of factors at play that can impact the timeline.
While the complexity of the product and the experience level of the team are two key variables, there are many other factors that can come into play as well.
For example, the availability of resources, the scale of the project, and the level of testing required can all contribute to the timeline.
On average, building an MVP can take anywhere from three to six months, though this can vary widely depending on the specifics of the project. While it can be tempting to rush through the MVP process in order to get your product to market as quickly as possible, taking the time to build a solid foundation will ultimately pay off in the long run.
Conclusion
MVP development is a crucial step for businesses and entrepreneurs to test their ideas, validate the product’s features, and collect feedback from early adopters. By following the steps mentioned above, you can build an MVP and launch your product quickly in the market.
An MVP is a minimum viable product with essential features to validate the idea, while a prototype is a preliminary version of the product that demonstrates the idea’s feasibility.
An MVP should have only essential features required to validate the idea and satisfy early adopters.
The cost to build an MVP can range from $10,000 to $50,000, depending on the complexity of the product and the features included.
An MVP is a version of the product with only essential features, while a final product has all the features and functionalities that the developers intended to include.
The essential features for an MVP should be those that solve the core problem for the target audience and provide enough value to satisfy early adopters.
To market an MVP, you can use various methods such as social media marketing, influencer marketing, email marketing, content marketing, and more.
The success of an MVP can be measured by analyzing user feedback, engagement metrics, retention rates, and conversion rates.





No Comments
Comments are closed.