Table of Contents
When you’re embarking on a new project, be it a website, mobile app, or physical product, you’ll often hear the terms “Product Design” and “UX Design” thrown around. Or rather, Product Design vs UX Design.
It’s crucial to understand the differences and similarities between these two disciplines to make informed decisions for your project’s success.
In this guide, we’ll break down Product Design and UX Design, explore their use cases, provide real-world examples, and help you decide which one is the best fit for your needs.
Therefore, with this being said, let’s get right into it:
What is Product Design?

Let’s understand the first element of product design vs UX Design.
This concept, in essence, is about creating tangible or digital products that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also functional and user-friendly.
Moreover, It’s a holistic approach that encompasses everything from the product’s appearance to its features and functionalities.
We know product design can often be a concept that’s hard to grasp, that’s why, we shall be discussing all you need to know about the same. This covers uses, principles, and many more.
As such, these are the things that you need to understand before you go on looking for top product design companies.
Industries That Use Product Design

Product Design is applied in various industries, including:
- Manufacturing
- Consumer Goods
- Automotive
- Industrial Design
And more, where physical products are created and improved.
Product Design Core Principles

Again, another important steps of getting your head around product design vs UX Design, you must understand the core principles.
When it comes to product design, there are fundamental principles that are like guiding stars to create products that truly resonate with you.
Let’s explore these core principles together:
01. User-Centered Design
At the heart of product design is you—the user. Every aspect of the product, from its form to its functionality, should revolve around making your life easier, more enjoyable, and more efficient.
02. Functionality
Think of functionality as the backbone of a product. It’s about ensuring that the product performs its intended tasks flawlessly and effectively, addressing your needs and solving your problems.
03. Aesthetics
Aesthetic appeal is important. Product designers strive to make products visually pleasing, evoking emotions and enhancing your overall experience. It’s like adding a touch of art to your everyday life.
04. Simplicity
Simplifying a product’s design is like decluttering a room. By removing unnecessary complexity and focusing on what truly matters, designers make the product more user-friendly and less intimidating.
05. Ergonomics
Ergonomics is all about making the product fit seamlessly into your life. Designers ensure that the product is comfortable to use, with well-placed buttons, easy-to-hold shapes, and intuitive controls.
06. Sustainability
Sustainability is a core principle that reflects the responsibility of product designers towards the environment. They consider materials, production processes, and the product’s lifecycle to minimize its ecological footprint.
07. Innovation
Innovation is like the engine that drives progress. Product designers are always looking for ways to improve, whether through cutting-edge technology, novel features, or creative solutions to old problems.
08. Accessibility
Just as a building should have ramps for everyone, products should be accessible to people of all abilities. Designers work to ensure that the product is usable by a diverse range of users.
09. Durability
Durability is essential to ensure that the product serves you for a long time. Designers choose robust materials and construction techniques to make the product withstand wear and tear.
10. Feedback and Iteration
The journey doesn’t end with the product’s release. Designers value your feedback and continuously iterate on the design based on real-world usage, making the product even better over time.
By embracing these core principles, product designers create products that not only meet your functional needs but also resonate with you on an emotional and aesthetic level.
Moreover, they strive to make your interactions with products seamless, enjoyable, and memorable, enhancing your daily life in meaningful ways.
Real-World Example of Product Design

It goes without saying one of the best ways to understand a concept is through example. That’s why we shall be going through a real-world example of product designing.
A real-world example of product design is the development of the iPhone by Apple Inc.
The iPhone is a groundbreaking product that has had a significant impact on the smartphone industry and technology as a whole.
Here’s an overview of the product design process for the iPhone:
- Understanding Users: Apple researched what users like you wanted in a phone, like combining music, internet, and calls in one device.
- Great Ideas: They brainstormed ideas and considered cool features, like touchscreens and sensors.
- Testing and Feedback: Apple built prototypes and asked people like you for feedback, fine-tuning the design.
- Easy to Use: They focused on making the iPhone easy for anyone to use with its iconic touch-based interface.
- Quality Matters: Apple used top-notch materials and precise manufacturing to ensure a premium look and feel.
- No Glitches: Rigorous testing ensured that the iPhone worked flawlessly, inside and out.
- Smart Software: They created iOS to work seamlessly with the hardware, giving you a smooth experience.
- Beautiful and Iconic: The iPhone’s clean, minimalist design became a symbol of Apple’s style.
- Big Launch: Apple launched the iPhone with excitement, showing how it could do more than just make calls.
Moving on, we shall be going through the entire product design process in the next step in a bid to better understand the entire product design vs UX Design conversation.
Product Design Process

So, what happens after you hire product designer? What happens is known as product design process.
And in his section of the blog, we shall be taking you through the detailed, process of product designing.
Therefore, let’s get right into it:
Step 1. Idea Generation – From Brainwaves to Brilliance
It starts with a lightbulb moment, perhaps during your morning coffee or a late-night brainstorming session.
You think, “What if…?” This is where your product design journey begins.
Step 2. Research – Digging for Insights
Next, you dive into research mode.
You’re like a detective gathering clues.
Moreover, You study your target audience, competitors, and market trends. It’s all about understanding the landscape.
Step 3. Conceptualization – Sketching the Blueprint
Armed with insights, you put pen to paper, or in today’s world, cursor to screen.
And you sketch out concepts and ideas, envisioning how your product will look and function.
Step 4. Prototyping – Bringing Ideas to Life
Now comes the exciting part. You turn those sketches into tangible prototypes.
Furthermore, it’s like creating a rough draft of your masterpiece, allowing you to see how things might work.
Step 5. Testing – The User’s Perspective
You put your prototypes in the hands of real users.
And you watch their reactions, listen to their feedback, and adjust your design based on their experiences.
Step 6. Refinement – Polishing the Gem
Back to the drawing board, but this time with the insights from testing.
Plus, you refine your design, tweaking details, and making improvements. It’s like polishing a precious gem to perfection.
Step 7. Final Design – Ready for the Spotlight
Your design is now ready to shine.
You create the final product, paying attention to every detail. It’s like getting dressed up for a special occasion.
Step 8. Production – Making It Real
The production phase is where your vision becomes reality.
Moreover, manufacturers or developers work their magic, bringing your design to life.
Step 9. Launch – Unveiling Your Creation
It’s like a grand premiere.
You introduce your product to the world, whether it’s a physical item on shelves or a digital wonder in app stores.
Step 10. Post-launch – Listening and Adapting
Your journey doesn’t end at launch.
And you keep a close ear to the ground, listening to user feedback, and making updates as needed. It’s a continuous cycle of improvement.
Throughout this process, your passion and creativity drive each step. Moreover, you’re on a journey to transform an idea into a tangible, user-friendly, and beautiful product that makes a difference in people’s lives. And that’s the magic of product design!
Now that we are done with the product design side of the product design vs UX Design contest, now we go to UX Designing.
What is UX Design?

We all often have heard of the term UI/UX Design. Especially if you are in tech-related field.
Coming to the point, UX Design, on the other hand, is all about enhancing the overall user experience of a product or service.
Moreover, it involves research, prototyping, and testing to ensure that the user’s journey is seamless and enjoyable.
Later down the blog, we shall be discussing all of that. But before that, let’s look at some industries that are using UX Designing.
Industries That Use UX Design
UX Design is commonly applied in the tech industry, covering:
- Web development
- Mobile app development
- Software development
And any field where digital interfaces and user experiences are crucial.
Now, with this out of the way, let’s look at the UX Design core principles in the section below.
UX Design Core Principles
When it comes to UX (User Experience) design, there are some core principles that are like guiding stars to create digital experiences that truly resonate with you.
Let’s dive into these principles together:
01. User-Centered Design
At the heart of UX design is you—the user.
Every decision, every interaction, and every element of a digital product should revolve around making your experience as smooth, efficient, and delightful as possible.
02. Usability
Think of usability as the user-friendliness factor.
Moreover, UX designers strive to make sure that using a website or app feels like second nature to you.
They want you to achieve your goals without any hassle.
03. Accessibility
Just as buildings have ramps for wheelchairs, digital products should be accessible to everyone.
And UX designers ensure that the experience accommodates people with disabilities, making it easier for everyone to use.
04. Consistency
UX designers aim for consistency in design elements and interactions.
When you encounter familiar patterns and layouts, it’s like revisiting a favorite place—you know exactly what to expect.
05. Clarity
Clear and concise communication is key. UX designers use language, icons, and visual cues that make it easy for you to understand how to navigate and use a product effectively.
06. Feedback and Affordance
When you click a button, you expect a response.
UX designers ensure that interactions provide feedback, like changing button colors when you hover over them.
Therefore, it’s like having a conversation with the product.
07. Flexibility
Not every user is the same.
And that’s why, UX designers create interfaces that allow you to personalize your experience, giving you choices and options to adapt the product to your preferences.
08. Simplicity
Simplifying the user experience is like decluttering a room.
Furthermore, UX designers remove unnecessary elements, focusing on what truly matters to help you achieve your goals without distractions.
09. Emotional Design
UX designers aim to elicit emotions that resonate with you.
Whether it’s joy, trust, or satisfaction, they want you to have a positive emotional connection with the product.
10. Continuous Improvement
UX design is a journey, not a destination.
Designers continually gather feedback, analyze data, and iterate on the user experience to keep making it better and more aligned with your evolving needs.
Real-World Example of UX Design
Just like we did in the former part of Product design vs UX Design debate, we shall be looking at an example of UX Design in real world scenario.
And this brings us to AirBnB
Have you ever used Airbnb to book a stay?
If so, you’ve experienced the power of UX (User Experience) design firsthand.
Let’s dive into how Airbnb’s user-friendly design makes your travel experiences extraordinary:
- Easy Search: A simple search bar helps you find places effortlessly.
- Custom Filters: Tailor your search with filters for a perfect fit.
- Vivid Imagery: High-quality photos and reviews paint a clear picture.
- Secure Booking: Trustworthy payment and support ensure peace of mind.
- Local Tips: Discover hidden gems with host recommendations.
- Personal Touch: Get personalized suggestions for future trips.
Airbnb’s UX design makes traveling a breeze, from booking to exploring local gems, creating memorable adventures along the way.
UX Design Process
Again to better understand the user experience designing, let’s look at the detailed UX design process below.
Each step well-described below:
Step 1. User Research – Getting to Know You
The first step is all about understanding you, the user. UX designers conduct research to learn about your needs, behaviors, and pain points.
Moreover, they might use surveys, interviews, and observations to gather insights.
Step 2. Information Architecture – Building the Blueprint
Imagine creating a blueprint for your dream home.
Therefore, UX designers work on structuring the information and content in a way that’s logical and easy to navigate.
This step sets the foundation for a seamless user experience.
Step 3. Wireframing and Prototyping – Sketching Out Ideas
Think of wireframes and prototypes as rough sketches of your design.
Designers use these to visualize layout, content placement, and interactions. It’s like testing the waters before diving in.
Step 4. User Testing – Your Opinion Matters
UX designers value your opinion.
Plus, They conduct usability tests where you interact with prototypes, and they watch how you navigate and gather feedback.
Your insights help refine the design.
Step 5. Visual Design – Adding the Beauty
This step is like adding a splash of color and decor to your home.
This is why, the designers focus on aesthetics, choosing fonts, colors, and graphics that align with the project’s goals and your preferences.
Step 6. Development – Bringing it to Life
Now, it’s time to build the actual digital product or website.
App developers take the design and turn it into a functional, interactive reality, just like bringing architectural plans to life.
Step 7. Testing and QA – Fine-Tuning the Details
Quality assurance is like making sure all the pieces of your home fit perfectly.
Moreover, UX designers and developers test every aspect of the product, fixing any bugs or issues that may arise.
Step 8. Launch – Opening the Doors
Launch day is like opening the doors to your dream home.
The product goes live, and users like you get to experience the results of all the hard work.
Step 9. Post-Launch Evaluation – Continuous Improvement
UX design doesn’t stop at launch.
Designers collect user feedback and monitor how the product performs.
They make updates and improvements to ensure it continues to meet your needs.
Step 10. Iteration – The Ongoing Journey
Lastly, UX design is an ongoing journey, like maintaining and upgrading your home.
Designers constantly iterate and refine the user experience based on changing needs and emerging trends.
With both end of product design vs UX Design out of the way, it’s time to look at the similarities you see in both these concepts.
Product Design vs UX Design Similarities
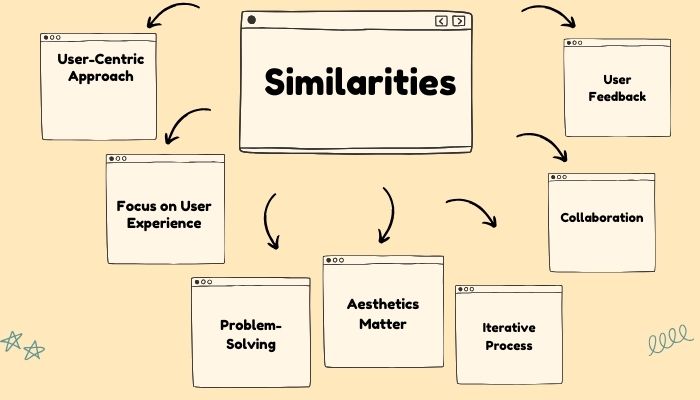
It goes without saying that product design vs UX Design seem like two entirely different process. And even though they are, they do share some similarities.
That’s exactly what we shall be discussing here. Let’s break it down for you in a way that’s easy to understand:
A. User-Centric Approach
In both Product Design and UX Design, your needs and preferences take center stage.
The goal is to create products and experiences that cater to your satisfaction and usability.
B. Focus on User Experience
Whether it’s crafting a physical product or designing a digital interface, both Product Design vs UX Design share a common focus on ensuring you have a positive and enjoyable experience.
C. Problem-Solving
Both disciplines involve identifying and addressing user-related issues or pain points.
Again, this means they’re dedicated to making your interactions smoother and more effective.
D. Aesthetics Matter
Both Product Design vs UX Design understand the importance of aesthetics. And they strive to make products and interfaces visually appealing, enhancing your overall satisfaction.
E. Iterative Process
They follow an iterative design process, which means they create prototypes, test them, and make continuous improvements. This ensures that the final product or interface meets your expectations.
F. Collaboration
Both fields require teamwork. Designers, researchers, engineers, and stakeholders come together to collaborate and make sure the end result aligns with your needs and desires.
G. User Feedback
To make informed decisions, both Product Design vs UX Design rely on your feedback and usability testing.
Moreover, they want to ensure that the end product or interface meets your expectations and provides a seamless experience.
In a nutshell, whether it’s Product Design or UX Design, they share a common mission: to enhance your satisfaction, whether you’re holding a physical product or navigating a digital interface.
Your needs are at the forefront of their efforts, making your experiences smoother and more enjoyable.
And now it’s time to look at the differences between them in the section below:
Product Design Vs UX Design Differences
Despite similarities between product design and UX Design, we should forget that the blog title has “vs”.
Therefore, it’s time to compare these two platforms with each other’s, as shown in the table below.
| Aspect | Product Design | UX Design |
| Primary Focus | Primarily concerned with the physical form, functionality, and aesthetics of a product, often tangible items. | Primarily focused on designing the overall user experience, particularly for digital interfaces and interactions. |
| Scope | Extends beyond digital products to encompass physical objects, industrial design, and manufacturing processes. | Primarily centered around digital products, websites, mobile apps, and software interfaces. |
| Design Elements | Emphasizes physical attributes like materials, ergonomics, and manufacturing processes. | Concentrates on user interface (UI) design, information architecture, and user interactions. |
| Tangibility | Deals with tangible, physical objects that you can touch, hold, and interact with in the real world. | Deals with intangible digital experiences, making it more abstract and virtual. |
| End Goals | Aims to create functional and aesthetically pleasing products that meet user needs in the physical world. | Aims to optimize the digital user journey, making it intuitive, efficient, and user-friendly. |
| Testing and Validation | Involves physical prototyping, material testing, and real-world usability trials. | Involves usability testing, wireframing, and digital prototypes to assess and refine the user interface. |
| Industry Applications | Applied across a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, consumer goods, and industrial design. | Commonly applied in the tech industry, web development, mobile app design, and software development. |
| Expertise Required | Requires knowledge of materials, manufacturing processes, and physical engineering. | Requires expertise in user research, information architecture, interaction design, and usability principles. |
| Deliverables | Often includes physical prototypes, CAD drawings, and specifications for manufacturing. | Includes wireframes, mockups, user flows, and design specifications for digital interfaces. |
| Timeframe | Typically involves longer development cycles due to physical production constraints. | Often features shorter development cycles, allowing for quicker iterations in digital environments. |
All in all, Product Design vs UX Design differ in their focus, scope, tangible vs. intangible nature, goals, testing methods, industry applications, required expertise, deliverables, and development timeframes.
Understanding these distinctions can help you appreciate how each field contributes to enhancing different aspects of the products and experiences you encounter in your daily life.
Now, if you want to develop an app or a product, it’s highly recommended that you consul a design company like We AppIt LLC that can help you with the same.
Conclusion
In the dynamic world of design, both Product Design vs UX Design play pivotal roles in shaping our interactions with the physical and digital realms. While they have distinct focuses and methodologies, their shared commitment to enhancing user experiences underscores their importance in creating products that are not only functional but also deeply satisfying. Whether in the physical or virtual domain, the principles and practices of these disciplines continue to shape the way we live, work, and engage with the world around us.




No Comments
Comments are closed.