Table of Contents
UI vs UX, are these two different things?
Well, we are all so habitual of hearing UI/UX Designing that most people forget these are two different concept.
User experience and user interface, as the name tells, stand as two different concept that works together. And not to mention, both of they are very-very important for various reasons.
If you are someone new to concept who want to learn more about the difference and importance, this blog is for you.
Here, we shall be discussing all you need to know about UI vs UX. Therefore, let’s get right into it:
Defining User Interface (UI)
Let’s start by defining user interface designing.
The term User interface (UI) refers to the visual and interactive elements of a digital product or service.
It encompasses the design, layout, and components that users interact with when navigating a website, mobile app, or any other digital platform.
UI focuses on creating an aesthetically pleasing and intuitive interface that is visually appealing, consistent, and easy to understand.
Now, there are a lot of UI design trends going on, but we won’t be getting to deep into that topic here.
Let’s move on and let’s look at some of the key elements of UI. Then we shall discuss the other aspect of UI vs UX, i.e. UX.
Key Elements of User Interface (UI)
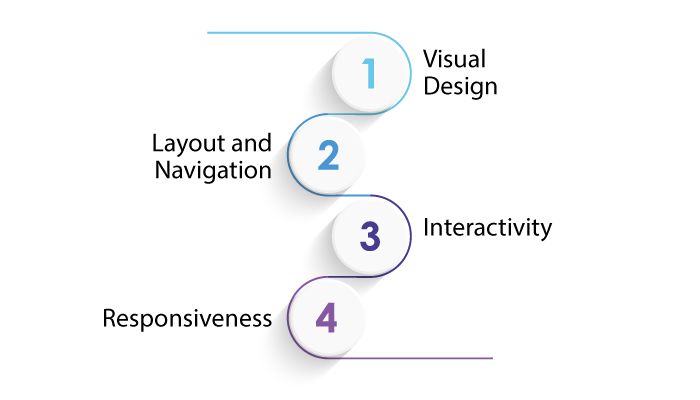
To understand user interface part of designing, you need to understand it’s different elements. Therefore, with this being said, let’s get right into it, the elements are, as mentioned below:
Visual Design
UI involves creating visually appealing layouts, color schemes, typography, icons, and graphics that align with the brand’s identity and resonate with the target audience.
Layout and Navigation
UI designers organize information and features in a logical and easy-to-navigate manner, ensuring users can find what they need without confusion or frustration.
Interactivity
UI designers design interactive elements such as buttons, forms, menus, and animations, aiming to enhance user engagement and provide clear feedback for user actions.
Responsiveness
With the rise of mobile devices, UI designers must ensure the interface is responsive and adaptable to different screen sizes and orientations.
With these out of the way, it’s time to look at the User experience part of UI vs UX in the section below:
Defining User Experience (UX)
User experience (UX) encompasses the overall experience a user has while interacting with a digital product or service.
It involves understanding user behavior, needs, and motivations to design a seamless and meaningful experience. UX focuses on creating products that are easy to use, efficient, enjoyable, and fulfill user expectations.
Now, there are lot of other things that you can learn about UX. For instance, UX storyboarding, UX Design frameworks, and so on.
As of now, we shall be discussing the different elements of user experience in next section.
Key Elements of User Experience (UX):
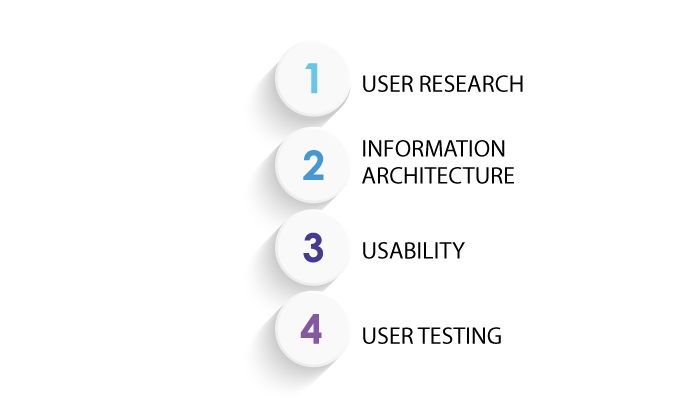
Just like discussed in user interface part of UI vs UX, we shall be discussing the differences of user experience below:
User Research
UX designers conduct user research, gather insights, and analyze user behaviors, needs, and preferences to inform the design process.
Information Architecture
UX designers structure the content, features, and functionalities of a product to ensure users can easily find and access relevant information.
Usability
UX designers aim to create products that are intuitive and easy to use, minimizing the learning curve and maximizing user efficiency.
User Testing
UX designers conduct usability testing and gather feedback from users to identify pain points, improve usability, and refine the overall user experience.
Now that we have discussed both sides of UI vs UX, it’s time to understand the importance. And we shall be doing just that in next section of the blog.
The Importance of UI and UX

Whether you are designing an app or going for product branding, UI and UX remains an important element. But why?
Well, we shall be discussing the important of UI and UX in this section of the blog, therefore, let’s get right into it.
First Impressions
UI vs UX are crucial in making a positive first impression. A well-designed UI captures users’ attention, while a smooth UX ensures users can easily accomplish their tasks, fostering trust and engagement with the product or service.
User Satisfaction
Effective UI vs UX contribute to user satisfaction. When users can easily navigate an interface, find what they need, and accomplish their goals efficiently, they are more likely to have a positive experience and develop loyalty towards the brand.
Increased Conversion Rates
A well-crafted UI vs UX can lead to improved conversion rates. By optimizing the user flow, reducing friction, and providing a pleasant experience, businesses can increase the likelihood of users completing desired actions, such as making a purchase or subscribing to a service.
Competitive Advantage
In a saturated digital market, UI vs UX can serve as a competitive advantage. A superior UI vs UX can differentiate a product or service from competitors, attracting and retaining users, and enhancing brand perception.
Customer Retention
UI vs UX play a significant role in customer retention. If users encounter frustration or confusion when interacting with a product, they are more likely to abandon it and seek alternatives. On the other hand, a delightful UI vs UX encourage users to return, increasing customer retention and fostering long-term relationships.
UI vs UX: The differences
Yes, UI vs UX are two different things, not complete different, but yes they aren’t the same.
Therefore, when comparing UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience), it’s important to consider their differences across various areas.
Let’s explore the distinctions between UI vs UX in different contexts:
Focus:
UI: UI primarily focuses on the design and presentation of the visual elements of a digital product. It involves creating attractive layouts, choosing colors, typography, and icons, and designing interactive components.
UX: UX focuses on the overall experience a user has while interacting with a digital product. It encompasses user research, information architecture, usability, and the emotional connection users establish with the product.
Design Process
UI: UI design often involves working with graphic design tools to create visually appealing interfaces. UI designers focus on aesthetics, ensuring consistency and harmony in the visual elements.
UX: UX design involves a more iterative and user-centered approach. It encompasses user research, wireframing, prototyping, and testing to gather insights and refine the user experience based on user feedback.
Goals
UI: The goal of UI is to create an interface that is visually pleasing, aesthetically appealing, and aligned with the brand’s identity. It aims to provide an intuitive and attractive environment for users.
UX: The goal of UX is to provide users with a seamless, efficient, and satisfying experience. UX designers aim to understand user needs, solve their problems, and create meaningful interactions that fulfill their goals.
Components
UI: UI includes elements such as layouts, color schemes, typography, icons, graphics, buttons, forms, and animations. These components are designed to be visually engaging and promote easy interaction.
UX: UX includes components such as user flows, information architecture, navigation menus, content hierarchy, and interactive features. These components focus on enhancing usability, task completion, and overall user satisfaction.
User Research
UI: While UI designers may consider user preferences and trends, their research is primarily focused on visual aspects like current design styles, color psychology, and branding guidelines.
UX: UX designers conduct extensive user research to understand user behaviors, motivations, and pain points. They employ techniques such as user interviews, surveys, and usability testing to gather insights and make informed design decisions.
Implementation
UI: UI designs are often implemented using front-end development technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. UI designers collaborate closely with developers to ensure the visual design is faithfully translated into a functional interface.
UX: UX design informs the overall product strategy and guides the decision-making process. It involves collaboration with various stakeholders, including developers, designers, product managers, and stakeholders, to ensure the user experience is effectively realized.
Now that you know what are the differences of these aspects of designing, you must be wondering, is there are similarities between UI and UX? Well, we shall be discussing just that in next section of the blog.
Are There Similarities in UI vs UX?

Now you have been through the major differences between UI and UX. However, there are a lot of people wondering, since they are used together, there must be some similarities too right? Well, yes there are.
In this section of the blog, we shall be going through the similarities between them. Therefore, with this being saidm let’s get right into it.
User-Centered Design
Both UI vs UX are rooted in the principles of user-centered design. They aim to create products and experiences that meet the needs, expectations, and goals of the users. Both disciplines prioritize understanding the target audience and designing with their preferences and behaviors in mind.
Collaboration
UI vs UX designers often collaborate closely throughout the design process. They work together to ensure that the visual design (UI) aligns with the overall user experience (UX) strategy. Collaboration fosters cohesion and consistency in the final product, ensuring that the interface and experience work seamlessly together.
Iterative Process
Both UI vs UX design involve an iterative approach. Designers continuously gather feedback, test prototypes, and make improvements based on user insights. This iterative process helps refine the UI vs UX over time, leading to better outcomes and enhanced user satisfaction.
Emotional Engagement
UI vs UX both consider the emotional aspects of the user experience. While UI focuses on creating visually appealing interfaces, UX seeks to evoke positive emotions and establish a connection between the user and the product. Both disciplines aim to create experiences that are enjoyable, engaging, and memorable.
User Testing
UI vs UX designers employ user testing techniques to gather feedback and validate their design decisions. Usability testing, user interviews, and surveys are used to understand how users interact with the product, identify pain points, and make informed design improvements. User testing ensures that both the UI vs UX meet user expectations and deliver a positive experience.
Impact on Business Goals
Both UI vs UX have a direct impact on the success of a digital product or service. A well-designed UI and a seamless UX contribute to customer satisfaction, which in turn leads to increased customer retention, improved conversion rates, and positive brand perception. Both disciplines play a crucial role in achieving business goals and fostering long-term success.
Conclusion
While UI vs UX are distinct disciplines, they are interconnected and essential for creating exceptional digital experiences. User interface (UI) focuses on the visual and interactive elements, ensuring a visually appealing and intuitive interface, while user experience (UX) encompasses the overall experience and satisfaction of users. By prioritizing both UI vs UX, businesses can deliver products and services that captivate users, foster loyalty, and stand out in a competitive digital landscape.
FAQ
UI (User Interface) focuses on the visual and interactive elements of a digital product, while UX (User Experience) encompasses the overall experience and satisfaction a user has while interacting with the product.
UI involves designing visually appealing layouts, selecting colors, typography, icons, and creating interactive elements such as buttons and forms.
UX entails user research, information architecture, usability testing, and creating a seamless and meaningful experience by understanding user behaviors and needs.
UI vs UX designers collaborate closely to ensure that the visual design (UI) aligns with the overall user experience strategy (UX), resulting in a cohesive and user-friendly product.
UI impacts user satisfaction by providing an aesthetically pleasing and intuitive interface, making it easier for users to navigate and interact with the product.
UX impacts business success by improving user satisfaction, leading to increased customer retention, higher conversion rates, and positive brand perception.
User testing helps gather feedback and validate design decisions in both UI vs UX, ensuring that the interface is visually appealing (UI) and the overall experience is user-friendly (UX).
While UI vs UX are distinct disciplines, they are interdependent. A well-designed UI without a seamless UX may result in frustration, and a great UX without an appealing UI may fail to engage users effectively.
A superior UI vs UX differentiate a product or service from competitors, attract and retain users, and enhance brand perception, providing a competitive advantage in the digital market.
UI vs UX are vital in creating exceptional digital experiences, improving user satisfaction, increasing conversions, fostering customer loyalty, and ultimately driving the success of a product or service.




No Comments
Comments are closed.